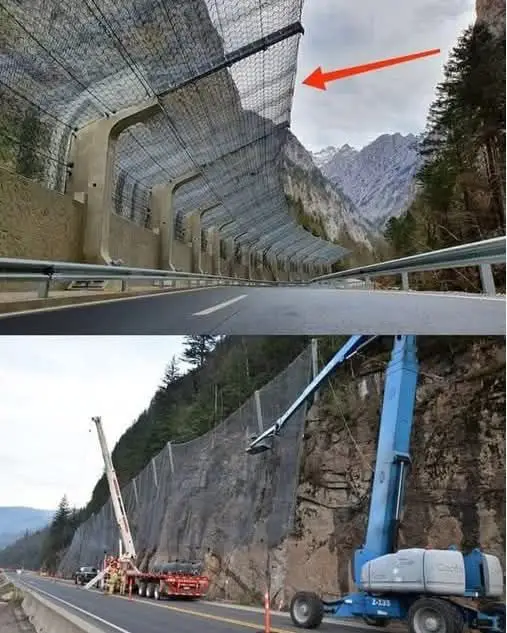
Mountain roads are often threatened by rockfalls, which can cause severe damage to infrastructure and endanger human lives. To mitigate this risk, engineers have developed various types of rockfall fences designed to absorb and deflect falling debris. Over time, these barriers have evolved to become more efficient and stronger, utilizing advanced materials and engineering techniques. This article explores different types of rockfall fences used globally to protect mountain roads.

1. Woven Wire Mesh Fences
Overview
Woven wire mesh fences are among the most commonly used rockfall barriers due to their flexibility and cost-effectiveness. These fences consist of steel wire mesh that is anchored to posts and secured with tension cables.
Advantages
- Lightweight and easy to install
- Provides flexibility to absorb rockfall impact
- Can be used on steep slopes
- Low maintenance costs
Applications
Woven wire mesh fences are commonly used in areas where frequent small-to-medium-sized rockfalls occur. They are often installed along highways, railways, and remote mountain roads.
2. High-Impact Dynamic Rockfall Barriers
Overview
Dynamic rockfall barriers are designed to absorb high-energy rockfalls using a system of steel posts, cables, and energy-absorbing panels. These fences are capable of withstanding large rock impacts by dissipating energy through their tensioned components.
Advantages
- High energy absorption (up to 5,000 kJ or more)
- Modular and scalable for different environments
- Can be installed on slopes and at road edges
- Minimal maintenance required
Applications
Dynamic barriers are used in high-risk zones where large and frequent rockfalls occur, such as in the Swiss Alps, the Rocky Mountains, and the Andes.
3. Rigid Rockfall Barriers
Overview
Rigid barriers are made from reinforced concrete or steel panels, offering maximum resistance to falling rocks. These barriers are designed to deflect rockfalls rather than absorb their energy.
Advantages
- Extremely durable and long-lasting
- Can be combined with retaining walls
- Provides solid protection in high-risk areas
Applications
These barriers are often installed in locations where road access is critical and where continuous maintenance is not feasible, such as tunnels and high-altitude passes.
4. Cable Net Fences
Overview
Cable net fences use high-tensile steel cables woven into a net structure that is anchored to the ground and supported by steel posts. These fences provide a high degree of flexibility while absorbing significant impact energy.
Advantages
- Capable of withstanding large rock impacts
- Allows drainage of water and debris
- Easily repairable after impact
Applications
Cable net fences are widely used in Japan, the United States, and Europe, where unpredictable rockfalls pose a major hazard.
Like Us on Facebook!
5. Hybrid Rockfall Protection Systems
Overview
Hybrid systems combine elements of dynamic barriers and passive mesh systems. These designs use steel cables, ring nets, and additional dampening elements to absorb and dissipate energy more effectively.
Subscribe Us on YouTube!
Advantages
- Provides superior energy dissipation
- More adaptable to site-specific conditions
- Reduces long-term maintenance costs
Applications
Hybrid systems are commonly used in locations with varying rockfall frequencies and sizes, such as Italy’s Dolomite region and the mountain roads of Canada.
6. Catchment Fences
Overview
Catchment fences are placed at the base of steep slopes to trap falling rocks before they reach the roadway. These fences are built with strong wire mesh or reinforced panels to contain large debris.
Advantages
- Effectively prevents rocks from reaching roads
- Reduces maintenance compared to slope stabilization
- Works well in conjunction with other barriers
Applications
Catchment fences are commonly used along highways in the Himalayas, the Sierra Nevada, and the Alps.
7. Snow and Rock Avalanche Barriers
Overview
In mountainous regions with heavy snowfall, rockfall barriers often double as avalanche protection systems. These fences are designed to withstand both rock impacts and snow pressure.
Advantages
- Dual functionality for rockfall and avalanche protection
- Reduces risk of road closures due to snow and rockfalls
- Strong and highly durable construction
Applications
Such barriers are found in the Swiss Alps, the Rocky Mountains, and northern Japan.
Conclusion
The evolution of rockfall fence designs has significantly improved road safety in mountainous regions worldwide. From traditional woven wire mesh to advanced dynamic and hybrid barriers, these solutions continue to protect infrastructure and human lives. As engineering advances, rockfall protection systems are becoming more resilient, adaptable, and cost-effective, ensuring safer travel in high-risk mountainous areas.