Spillways are critical components of dam infrastructure, designed to manage water flow and ensure the safety of reservoirs, waterways, and surrounding communities. A spillway’s effectiveness largely depends on its gates, which are the adjustable barriers that control the amount of water leaving the reservoir. This article delves into the fascinating world of spillway gates, explaining their design, operation, and significance.

What is a Spillway Gate?
A spillway gate is a movable structure used to regulate water flow in reservoirs, rivers, and streams. It serves a vital role in controlling water discharge during normal operations and flood conditions. By adjusting the opening between the gate and the reservoir, operators can control the volume of water released downstream. When fully closed, these gates act as robust barriers, holding back immense water pressure.
Types of Spillway Gates: An Overview
Spillway gates are designed to meet diverse operational and environmental requirements. These gates can be broadly categorized based on their operational mechanisms: gravity-based, hydraulic-based, and mechanical-based systems.
- Gravity-Based Gates: Operate using the gate’s weight to open and close, relying on the natural force of gravity.
- Hydraulic-Based Gates: Use hydraulic systems, including air and water chambers, to control gate movement with precision.
- Mechanical-Based Gates: Employ motors or mechanical systems to adjust the gate’s position.
While these classifications provide a broad understanding, spillway gates are more commonly recognized by their specific designs and applications. Below are detailed explanations of various gate types.
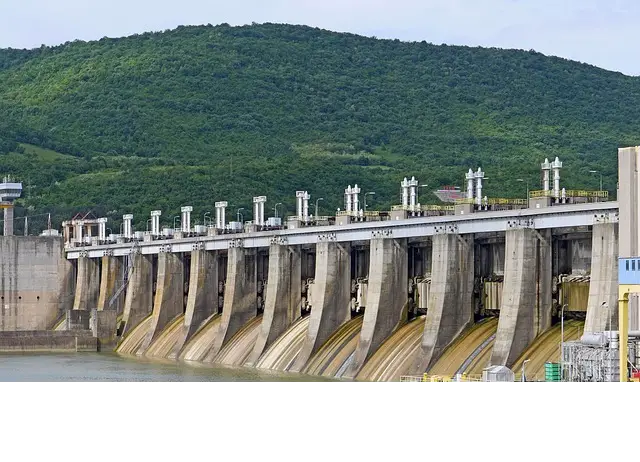

1. Sluice Gates
Sluice gates are versatile and widely used in dams and reservoirs. These gates feature a hinged design that allows operators to control water levels with precision. By lifting or lowering the gate, water can be released or retained as needed.
Key Features:
- Hinged design for flexibility.
- Accurate water level management.
- Durable and adaptable, making them ideal for various applications, including flood control and irrigation.
2. Slide Gates
Slide gates operate with a simple sliding mechanism, making them user-friendly and cost-effective. They require minimal equipment and are often employed in small-scale water projects.
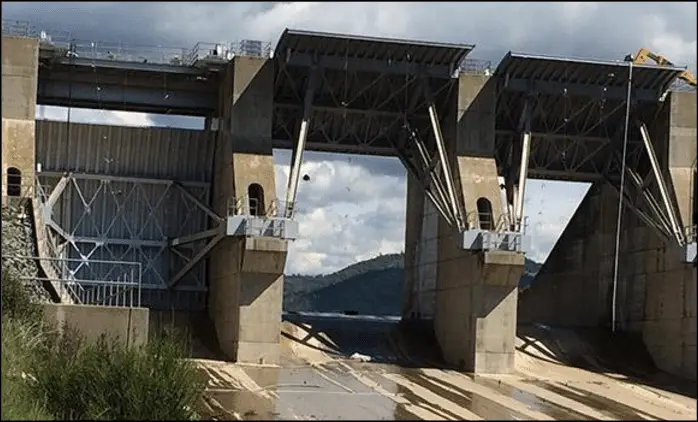

Key Features:
- Smooth sliding action for easy operation.
- Minimal maintenance requirements.
- Popular in irrigation systems and small reservoirs.
3. Crest Gates
Crest gates are bottom-hinged structures designed to handle challenging conditions, such as ice buildup or floating debris. These gates tilt upward or downward to regulate water flow efficiently.
Like Us on Facebook!
Key Features:
Subscribe Us on YouTube!
- Compact design for areas prone to debris accumulation.
- Efficient operation under hydraulic pressure.
- Reliable performance in extreme conditions.
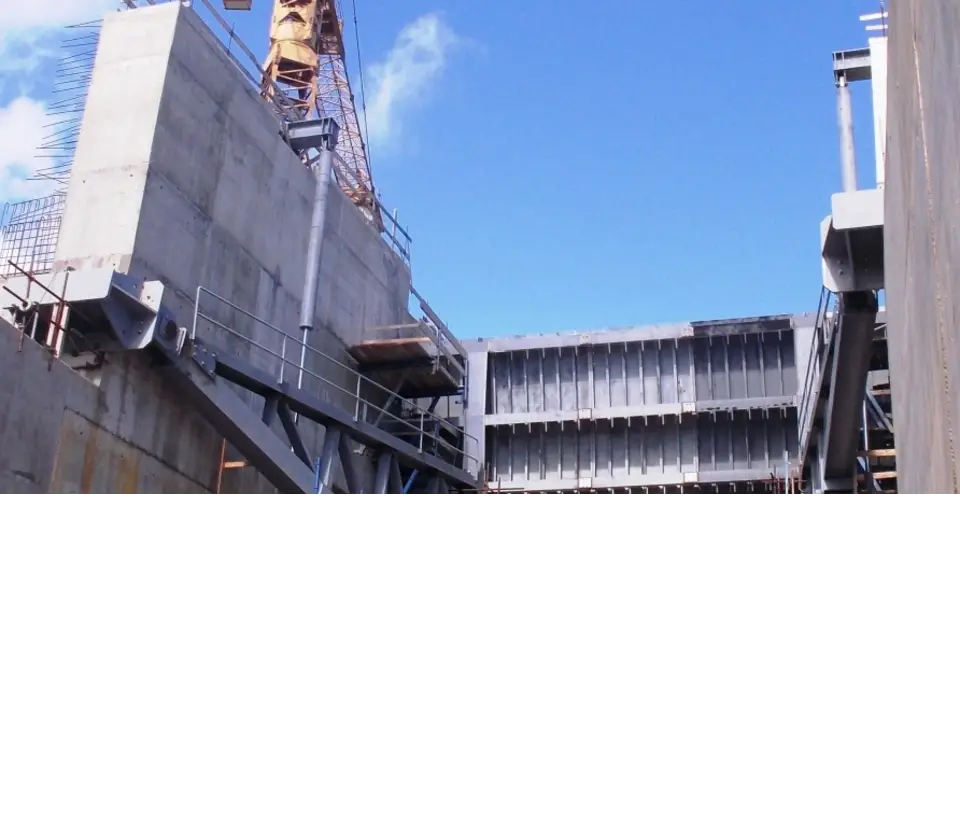

4. Radial (Tainter) Gates
Radial gates, also known as tainter gates, are curved structures that evenly distribute water pressure. This design minimizes stress on the gate components and simplifies operation.
Key Features:
- Curved design for balanced pressure distribution.
- Commonly used in large dams.
- Capable of managing immense water loads.
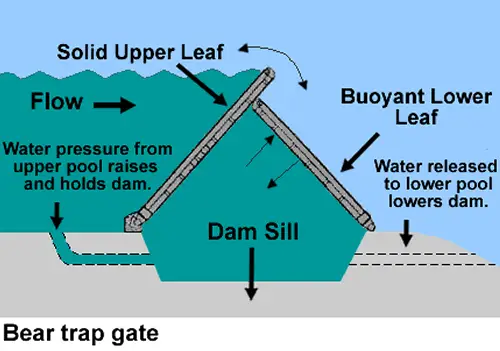
5. Bear Trap Gates
Bear trap gates consist of overlapping hinged leaves, offering precise control over water flow. Their intricate design ensures excellent sealing, even under demanding conditions.
Key Features:
- Exceptional precision in flow control.
- Advanced design for challenging environments.
- Frequently used in locks and specialized water diversion projects.

6. Drum Gates
Drum gates are hollow, buoyant structures hinged at the top of the dam. Their operation relies on adjusting buoyancy to raise or lower the gate with remarkable accuracy.
Key Features:
- Floating design for energy-efficient operation.
- Ideal for maintaining specific water levels in reservoirs.
- Precise control ensures safety and operational efficiency.
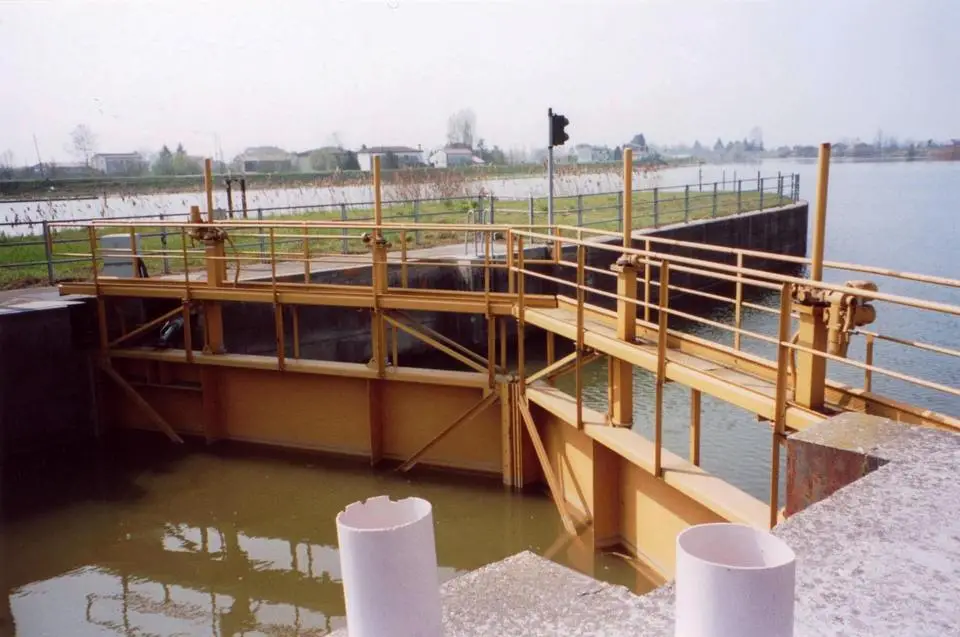

7. Miter Gates
Miter gates are most commonly found in canals and waterways. They consist of two leaves that meet at an angle, forming a V-shape when closed. This design effectively distributes water pressure, making them durable and reliable.
Key Features:
- Effective water pressure distribution.
- Essential for navigation systems in waterways.
- Ensures safe passage for vessels transitioning between different water levels.
Importance of Spillway Gates
Spillway gates play an indispensable role in water management systems. Their functions include:
- Flood Control: Preventing disasters by releasing excess water during high inflows.
- Water Regulation: Managing reservoir levels to ensure a steady supply for irrigation, drinking water, and hydropower.
- Environmental Protection: Minimizing downstream erosion and maintaining ecological balance.
Engineering Marvels in Action
From controlling water flow to safeguarding communities, spillway gates exemplify engineering excellence. Modern designs incorporate advanced materials and mechanisms to ensure reliability and efficiency under extreme conditions.
For instance, radial gates in large dams like the Garrison Dam on the Missouri River manage massive water volumes, while drum gates in reservoirs precisely maintain water levels. Each type of gate is uniquely tailored to its environment, making it an integral part of dam infrastructure.
Conclusion
Spillway gates may not be the stars of dam engineering, but their contribution is vital. These structures embody the ingenuity of modern engineering, ensuring the safety, functionality, and sustainability of water management systems worldwide.
If you enjoyed this deep dive into spillway gates, be sure to explore more about the fascinating world of engineering. Don’t forget to share this article and spark curiosity about the wonders of infrastructure.
























