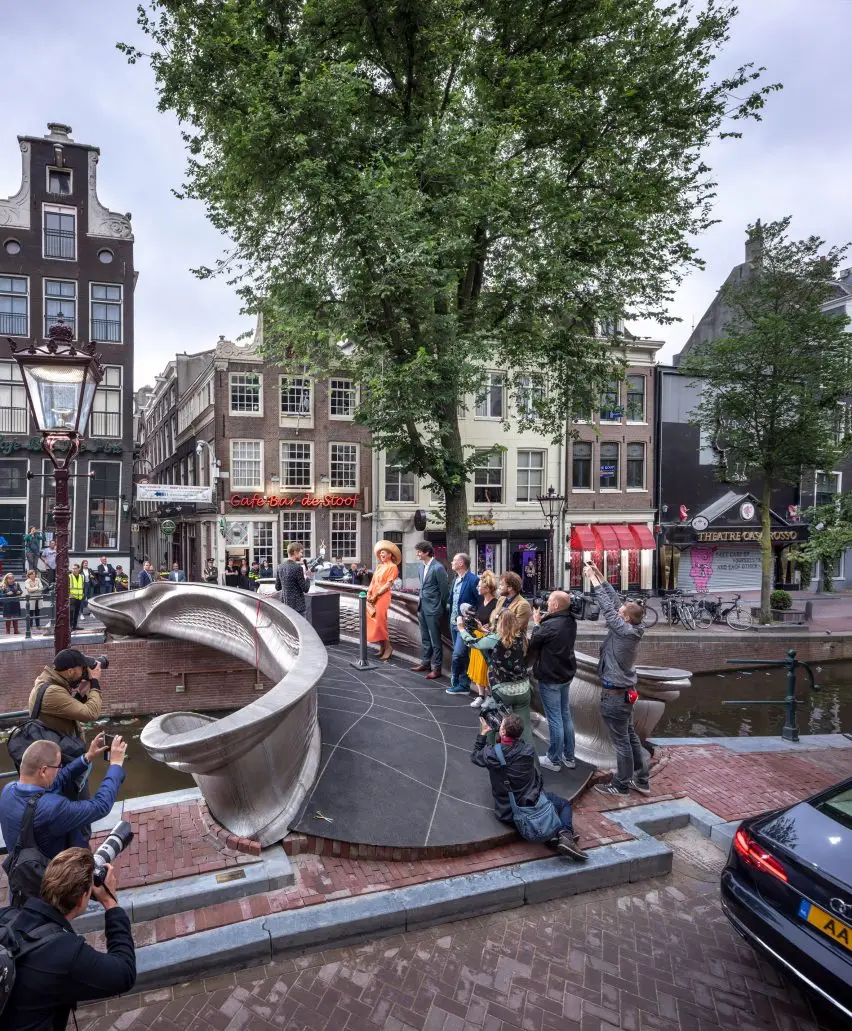
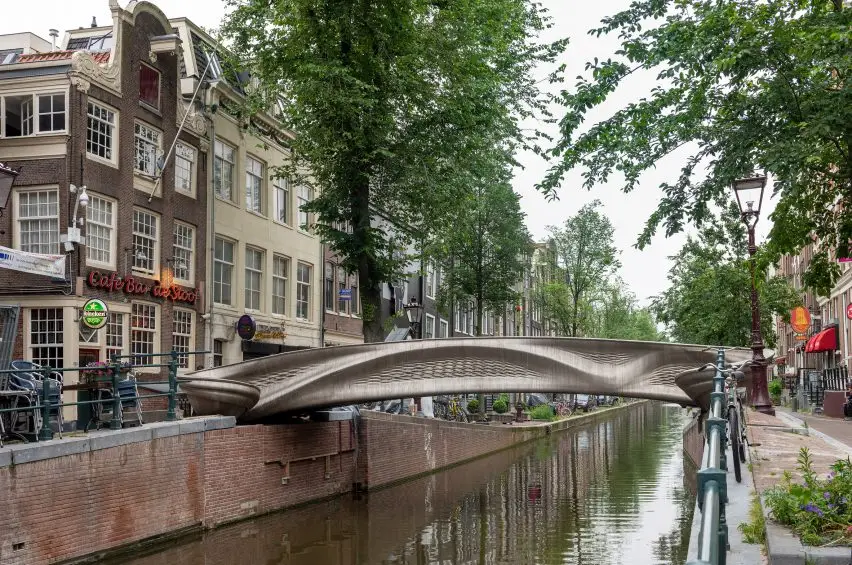
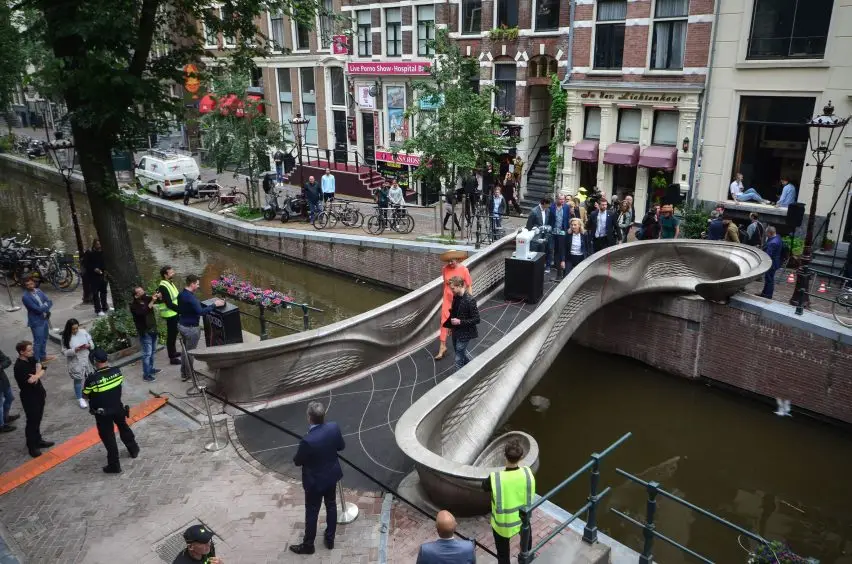
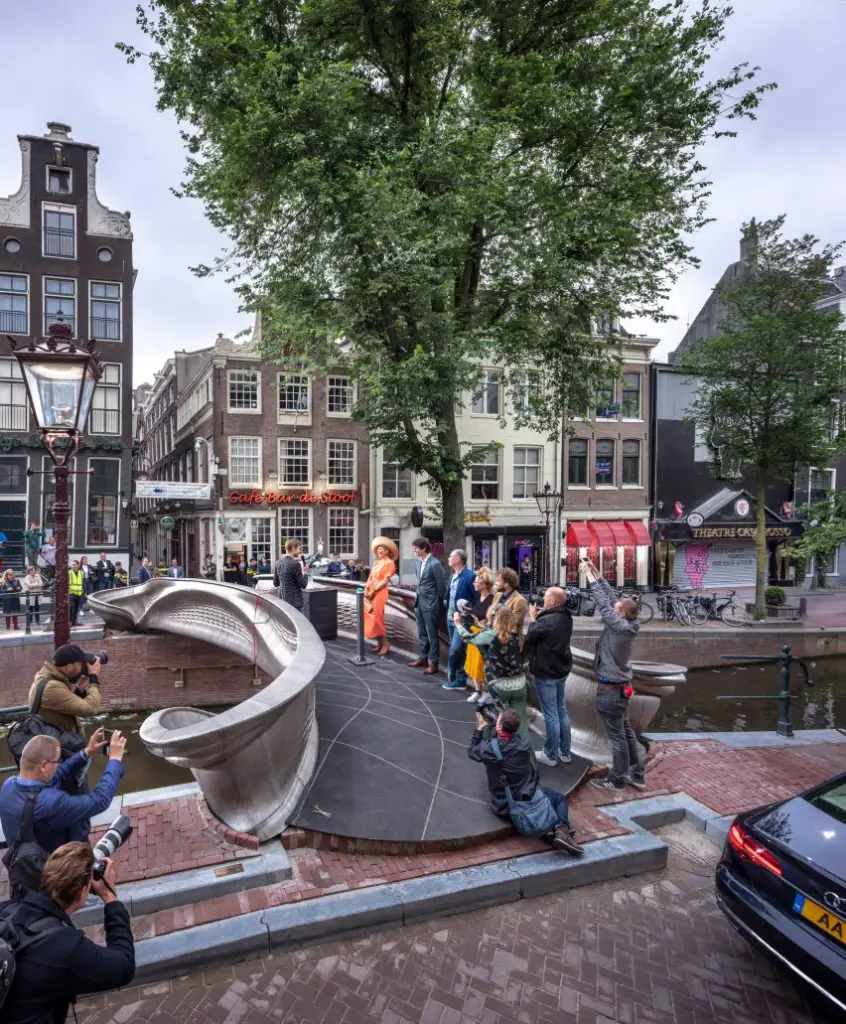
The MX3D Bridge, located in Amsterdam’s iconic Red Light District, stands as a testament to innovation, design, and advanced engineering. This 12-meter pedestrian bridge is the first of its kind, showcasing the potential of 3D printing technology in architecture and infrastructure. Designed by visionary Dutch designer Joris Laarman and constructed by the robotics company MX3D, the bridge combines futuristic technology with practical urban functionality.

A Revolution in Bridge Construction
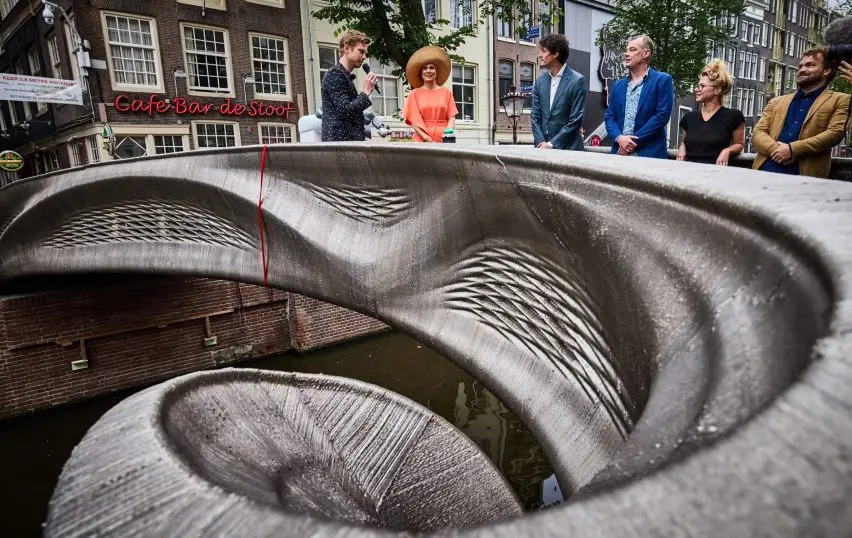
The MX3D Bridge is not just a structure; it is a marvel of modern engineering. Unlike conventional bridges, which rely on traditional construction methods, this bridge was created using six-axis robotic arms. These arms printed the bridge layer by layer, forming its unique S-shaped structure with remarkable precision.
The entire process took over six months to complete and involved printing stainless steel sections in a factory. This method not only minimized waste but also allowed for a high degree of customization, enabling the designers to incorporate intricate details that would be challenging to achieve using traditional methods.

Innovative Design with Lattice-Style Balustrades
One of the most striking features of the MX3D Bridge is its balustrades, which are adorned with lattice-style perforations. These patterns were crafted using parametric modeling software, a tool that allows designers to experiment with complex geometries and create highly optimized structures. The result is an elegant yet robust design that adds a modern aesthetic to the historic Red Light District.

Technology Meets Practicality
The construction of the MX3D Bridge highlights the seamless integration of robotics and 3D printing in large-scale projects. By utilizing six-axis robotic arms, the engineers achieved unparalleled flexibility in shaping the bridge’s intricate curves. The use of stainless steel ensures durability and longevity, making the bridge not only a design statement but also a functional piece of infrastructure.
A Bridge with Intelligence
What sets the MX3D Bridge apart from conventional structures is its smart capabilities. Equipped with an array of sensors, the bridge is designed to collect data on its performance, health, and environmental conditions. These sensors monitor aspects such as load capacity, vibrations, and temperature changes.
The collected data feeds into a digital twin, a virtual replica of the bridge that allows engineers to analyze its real-time condition. This continuous monitoring system ensures that any potential issues can be identified and addressed promptly, enhancing safety and extending the bridge’s lifespan.

A Landmark in Urban Innovation
The MX3D Bridge is more than just a pedestrian pathway; it is a symbol of how technology can redefine urban spaces. Situated in one of Amsterdam’s most visited areas, the bridge blends seamlessly with its surroundings while also serving as a beacon of innovation. Its creation marks a significant step forward in the use of 3D printing for practical applications, paving the way for future projects that prioritize sustainability, efficiency, and creativity.
Conclusion
The MX3D Bridge in Amsterdam is a groundbreaking achievement that demonstrates the immense potential of robotics and 3D printing in modern construction. By combining cutting-edge technology with artistic design, the bridge offers a glimpse into the future of infrastructure development. It not only connects two sides of a canal but also bridges the gap between innovation and functionality, inspiring cities worldwide to rethink how we build for the future.