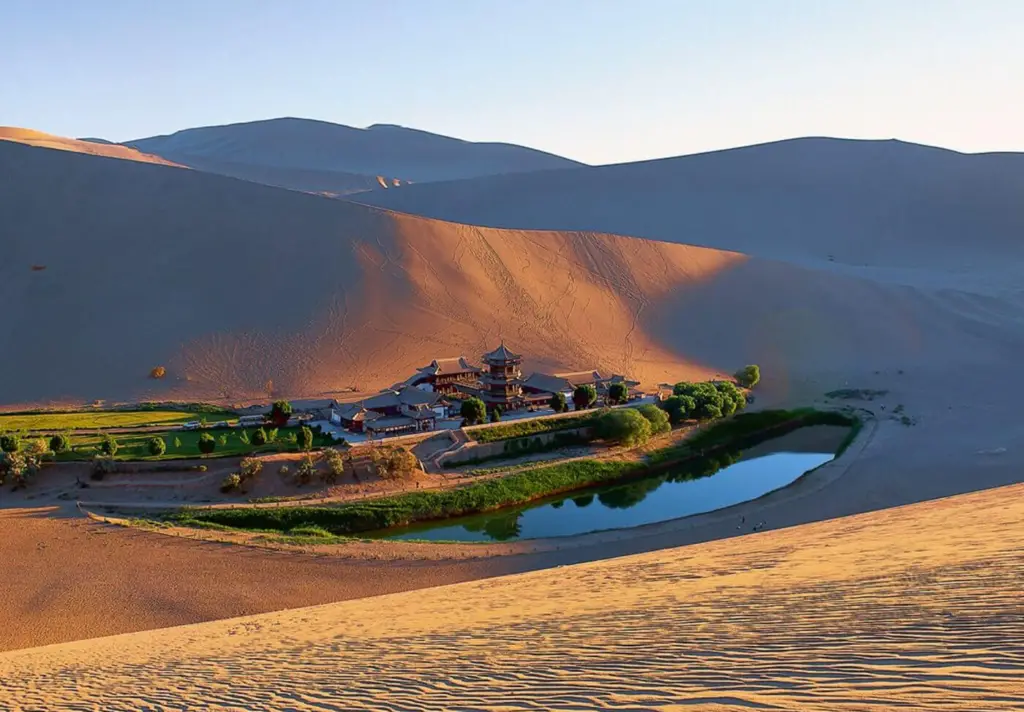
Located in the heart of the Gobi Desert, China, Moon Lake (also known as Yueyaquan) is a breathtaking natural wonder that continues to captivate travelers and historians alike. This crescent-shaped oasis, surrounded by towering sand dunes, stands as a testament to the resilience of nature and the ingenuity of human intervention.

The Crescent Shaped Beauty
Moon Lake’s crescent shape is what makes it so unique. Stretching across the desert landscape, the lake’s distinctive form has been preserved for over 2,000 years, despite being in one of the world’s most arid regions. Surrounded by the ever-shifting sands of the Gobi Desert, this natural formation is an oasis that has endured through centuries of change.
The lake’s preservation is not entirely due to nature alone. It has been carefully maintained through a combination of groundwater and modern conservation efforts, which prevent the lake from drying up and turning into part of the desert’s vast, barren expanse.

A Key Stop on the Silk Road
Moon Lake has been a critical landmark for centuries, especially for travelers on the Silk Road, the ancient trade route that connected the East to the West. Traders, merchants, and travelers would stop here to rest, refresh, and replenish supplies on their long journey through the desert. The lake’s historical significance as a strategic oasis has made it a vital point in China’s cultural and commercial history.
How Moon Lake Survives in the Arid Gobi Desert
Despite the harsh conditions of the Gobi Desert, Moon Lake remains a thriving oasis thanks to two primary factors: groundwater and human preservation efforts.
- Groundwater: Beneath the surface, natural aquifers feed into the lake, helping to sustain it even in the face of desertification.
- Conservation: Recent human interventions, including water management practices, have been implemented to ensure the lake does not shrink or disappear. These conservation efforts include water diversion systems and methods to control the flow of sand that threatens to cover the lake over time.
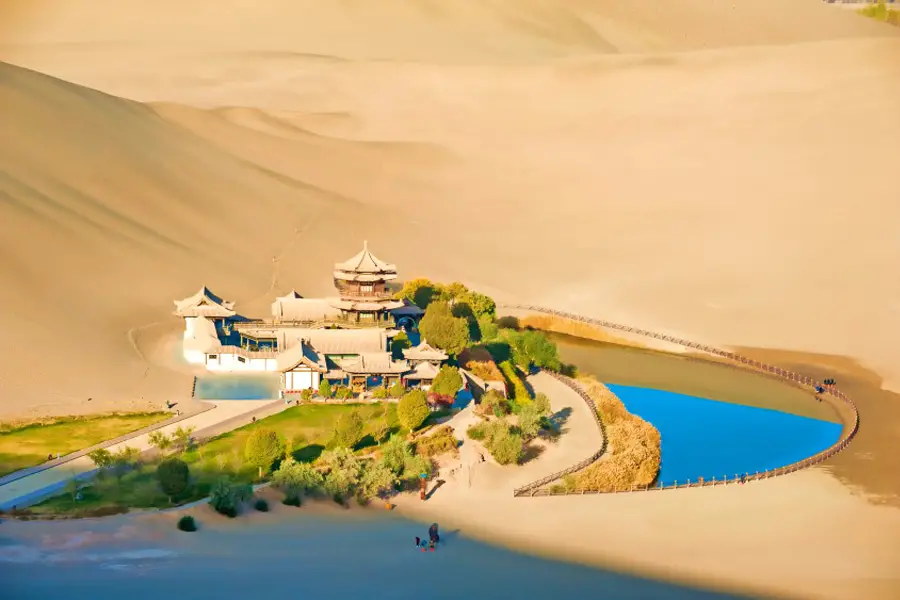

The Historical and Cultural Importance
Beyond its stunning beauty, Moon Lake holds deep historical and cultural significance. Its role as a key stop along the Silk Road has made it a crossroads of cultures and trade for centuries. The surrounding area is rich in archaeological and cultural relics, and visitors can explore the historical sites nearby to get a glimpse into the lives of ancient travelers.
A Modern Tourist Destination
Today, Moon Lake is a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from all over the world. Its unique beauty, historical importance, and the serenity it offers in the midst of the vast desert make it a standout location for those interested in both natural wonders and history. Tourists can walk along the shores of the lake, admire the towering sand dunes, and take in the picturesque landscape that has remained largely unchanged for millennia.
Conclusion
Moon Lake, nestled in the Gobi Desert, is more than just a beautiful oasis—it’s a living symbol of resilience. Its crescent shape, preserved for over 2,000 years, stands as a testament to the enduring power of both natural forces and human effort. As a key point on the ancient Silk Road, it has witnessed the movement of goods, ideas, and cultures across continents. Today, it remains an enchanting destination, drawing travelers from all over the world to experience its timeless beauty.