The Pantheon of Rome, an iconic architectural masterpiece, stands as a testament to the ingenuity and advanced engineering of ancient Roman civilization. Built nearly two millennia ago, this historic structure remains one of the most well-preserved monuments of Ancient Rome, admired not only for its aesthetic grandeur but also for its innovative solutions to architectural challenges.
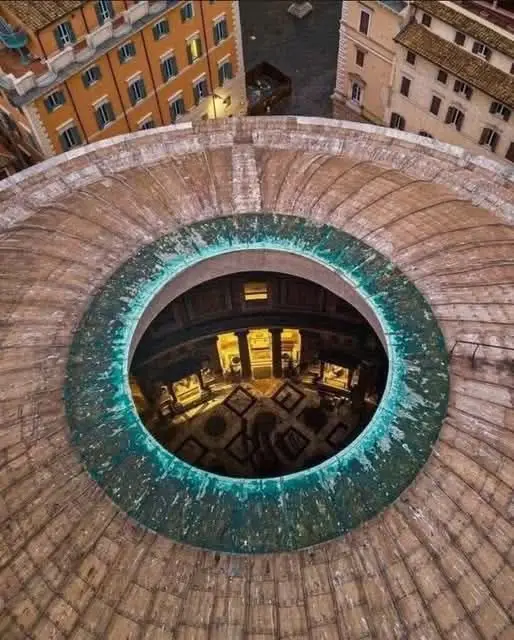
One of the most fascinating aspects of the Pantheon is its ability to manage rainwater effectively, even with the presence of its famous oculus—a massive circular opening at the center of the dome. Measuring 8 meters (26 feet) in diameter, the oculus serves as both a source of natural light and ventilation, creating a connection between the interior of the Pantheon and the sky above. However, the oculus also allows rainwater to enter the building during inclement weather, posing a unique design challenge for the architects of the time.

A Genius Solution: Subtly Convex Flooring
To address the issue of rainwater, the Romans incorporated a remarkable yet subtle feature into the Pantheon’s floor. The surface of the floor was designed to be slightly convex, almost imperceptible to the naked eye. This gentle slope enables rainwater to flow naturally toward a network of drainage points.
Strategically placed across the floor are 22 drainage holes, with two located directly beneath the oculus. The remaining holes are distributed between the center and the walls, ensuring that water is collected efficiently regardless of its point of entry. This meticulous arrangement prevents any pooling of water, preserving the integrity of the floor and maintaining the comfort of those inside.
Integration with Rome’s Sewer System
The drainage system of the Pantheon does not end within the building. The collected water is funneled into an underground drainage network, which is connected to the city’s extensive sewer system. This seamless integration reflects the Romans’ mastery of urban infrastructure, allowing the Pantheon to remain dry even during heavy storms. By redirecting the water safely away from the structure, the engineers ensured the building’s longevity and usability.
A Reflection of Roman Ingenuity
The rainwater management system of the Pantheon exemplifies the Romans’ unparalleled ability to merge functionality with architectural beauty. While the convex floor and drainage holes are practical elements, they are so skillfully incorporated into the design that they go unnoticed by most visitors. This combination of utility and elegance underscores the sophistication of Roman engineering and their commitment to problem-solving through innovation.
The Legacy of the Pantheon
The Pantheon continues to inspire architects, engineers, and historians around the world. Its enduring presence serves as a reminder of the remarkable capabilities of ancient civilizations. The solution to managing rainwater through clever design and integration with urban infrastructure highlights the foresight and ingenuity that have become synonymous with Roman construction.
As we admire the Pantheon today, we not only celebrate its visual and historical significance but also the timeless lessons it offers in engineering excellence.