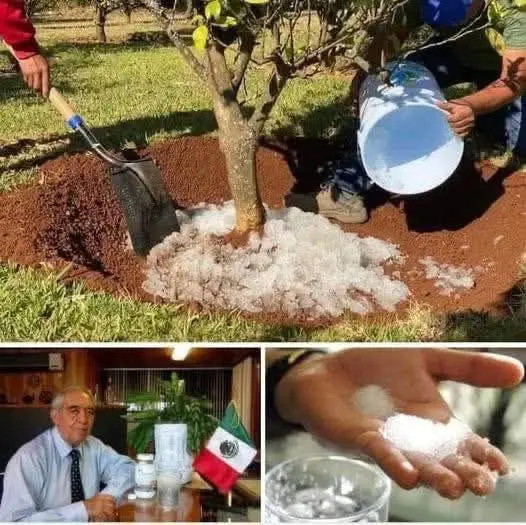
Water scarcity is one of the most pressing global challenges, particularly in regions dependent on agriculture. Recognizing this issue, Mexican engineer Sergio Jesus Rico Velasco has pioneered an innovative approach to water conservation that could transform agricultural practices worldwide. This groundbreaking solution uses potassium acrylate, a biodegradable polymer, to convert rainwater into a solid, gel-like resource capable of retaining moisture for extended periods.

The Birth of an Ingenious Idea
Necessity often drives innovation, and Velasco’s invention is no exception. In arid and semi-arid regions, erratic rainfall and prolonged dry spells create immense challenges for farmers. Conventional irrigation methods, while effective, are costly and often inaccessible to small-scale farmers. Velasco sought to bridge this gap with an affordable, efficient, and environmentally friendly solution.
His creation, potassium acrylate, represents a paradigm shift in water management. By capturing and storing rainwater directly in the soil, this polymer addresses one of agriculture’s most critical pain points: inconsistent water supply.
What is Potassium Acrylate?
Potassium acrylate is a powdered polymer with an extraordinary ability to absorb water. When exposed to rainwater, it undergoes a chemical transformation, becoming a gel-like substance capable of holding up to 210 times its weight in water. This gel retains its hydration for an impressive 41 days, gradually releasing moisture to the surrounding soil.
Unlike traditional water storage solutions such as reservoirs or tanks, this polymer integrates seamlessly into the natural ecosystem. It ensures localized water management, delivering hydration directly to plant roots without requiring expensive infrastructure.
Unpacking the Science
The polymer’s unique properties stem from its molecular structure, which binds water molecules within a stable gel matrix. This structure prevents water from evaporating or seeping away, making it an incredibly efficient storage medium.
Additionally, potassium acrylate is biodegradable, meaning it decomposes naturally over time without leaving harmful residues in the soil. This feature sets it apart from synthetic water retention products, which often have long-term environmental consequences.
Transforming Agriculture in Water-Stressed Regions
This technology has immense potential for regions plagued by unpredictable rainfall and droughts. Farmers in such areas face significant challenges, including crop failure, reduced yields, and increased costs. The introduction of potassium acrylate can address these issues in several ways:
- Boosting Crop Growth: By ensuring a consistent supply of moisture, the polymer promotes healthy plant development, even in adverse conditions.
- Reducing Water Usage: Studies indicate that this technology can lower water consumption in agriculture by up to 92%, a staggering reduction that conserves valuable resources.
- Lowering Costs: With decreased reliance on irrigation systems, farmers save money on water, labor, and equipment. This is particularly beneficial for smallholder farmers who often operate on tight budgets.
Environmental Benefits
The environmental implications of this invention are equally compelling. Potassium acrylate minimizes water wastage through evaporation or runoff, allowing farmers to make the most of every drop of rainwater. Its biodegradable nature ensures it integrates harmoniously into ecosystems, avoiding pollution or soil degradation.
Like Us on Facebook!
Additionally, by reducing water consumption, the polymer helps conserve freshwater resources, alleviating pressure on rivers, lakes, and aquifers. This is especially crucial in regions where over-extraction has led to dwindling water supplies and ecological imbalances.
Subscribe Us on YouTube!
Scaling Up: Challenges and Opportunities
While potassium acrylate has demonstrated remarkable potential, its success depends on widespread adoption. Key challenges include:
- Raising Awareness: Farmers and policymakers need to be educated about the benefits and applications of this technology.
- Ensuring Accessibility: The polymer must be produced and distributed affordably to reach communities that need it most.
- Encouraging Investment: Governments, NGOs, and private entities must collaborate to fund the development and deployment of this innovation.
A Vision for the Future
Velasco’s invention is more than just a technological advancement; it’s a beacon of hope for millions of farmers struggling to adapt to climate change. By supporting this project and others like it, we can pave the way for a sustainable agricultural future.
As global water resources become increasingly strained, innovative solutions like potassium acrylate offer a lifeline. They demonstrate how science and creativity can address some of humanity’s most urgent challenges, ensuring food security, economic stability, and environmental preservation.
Conclusion: Supporting Innovation for a Better Tomorrow
The journey of potassium acrylate from concept to implementation is a testament to human ingenuity. It reminds us of the importance of investing in ideas that can change lives, especially in vulnerable communities.
Let us advocate for and invest in sustainable technologies that protect our planet’s most precious resource—water. Together, we can create a future where no farmer has to choose between growing crops and conserving water.